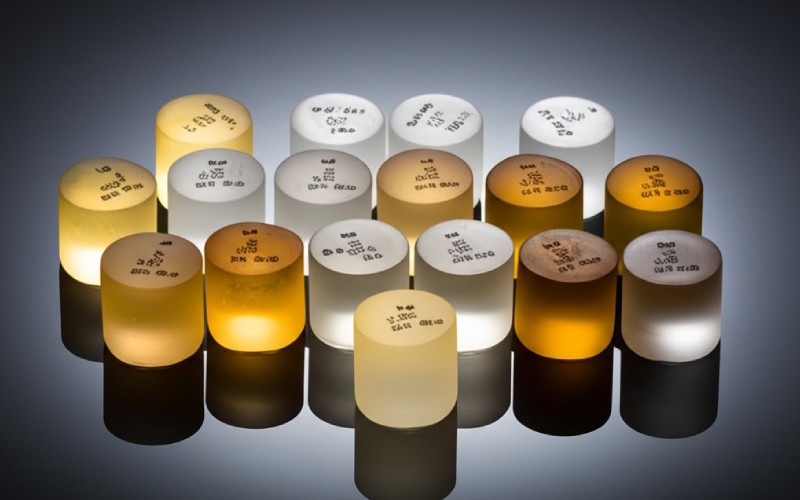
Emax: Scoprire la vera forza di un materiale in disilicato di litio come LiSi Press
Questo lithium disilicate material, Emax, isn’t just another glass-ceramic; it was a revolution in a small ingot. It blended strength and beauty in a way I had never seen before.
In this post, we’ll explore what makes this material, Emax, so special. We will look at its amazing resistenza alla flessione and how it gets that strength from its tiny crystal structure. If you are a dentist, a lab technician, or even a patient curious about the corona in your mouth, this article is for you. I’ll break down the science into simple terms and share what I know about this game-changing material, including other great products like LiSi Press.
Indice dei contenuti
What Is Lithium Disilicate, Anyway?
Let’s start with the basics. What is disilicato di litio? At its heart, it’s a type of glass-ceramic. Think of it as a special kind of glass filled with a huge number of tiny, needle-shaped crystals. The specific chemical formula is Li2Si2O5. This is important because it’s the key to its strength. These ceramica are part of a family of materiali dentali that have transformed how we restore teeth. The company Ivoclar Vivadent was a true pioneer in this field, and they really set the standard for what these materials could do.
Prima disilicato di litio, il nostro all-ceramic options were mostly weaker porcellana. They looked nice but could chip easily. This new lithium disilicate glass ceramic promised both beauty and power. It has excellent biocompatibilità, which means it’s safe and gets along well with the tissues in your mouth. This makes it a top choice in odontoiatria restaurativa. Il disilicato di litio itself is very stable.
Questi materiali ceramici are made through a controlled process of heating. This process creates a dense network of Li2Si2O5 crystals inside a glassy matrix. This structure is what stops cracks from spreading. So, when you choose a disilicato di litio corona, you’re getting a material that is designed from the molecule up to be tough and long-lasting. It’s one of the most trusted materials available for dental restorations oggi. Lithium disilicate is also known for its great bond to struttura del dente.
Why Is Emax So Popular in Modern Dentistry?
So why did Emax become the celebrity of the odontoiatria world? For example, a patient with a cracked front tooth needs a perfect, estetico result. A traditional porcellana faccetta feels risky. A stronger material like zirconia wouldn’t have the same traslucenza. When choosing to use an Emax restauro, the result is incredible. You can’t tell which tooth is the corona and which were natural.
The popularity of Emax comes from this amazing balance. It has the high resistenza alla flessione needed for a posteriore tooth but also the beautiful esthetics needed for an anterior faccetta. This versatility is a huge advantage. You can use this single lithium disilicate material for a wide range of jobs, from a full corona to a thin faccetta or even an inlay. This makes life easier for both the dentist and the laboratorio odontotecnico. The material gives us confidence that the restauro will look good and last for a very long time.
It’s one of the most commonly used all-ceramic materials for a reason. Emax allows for minimally invasive restorations. This means we can save more of the natural struttura del dente, which is always the goal. The material can be made very thin, as little as 1.0 mm per un corona, yet still be incredibly strong. This combination of features makes Emax a go-to choice for so many situations in odontoiatria. It truly delivers on its promise of a strong and beautiful smile.
How Strong Is Lithium Disilicate? Let’s Talk Flexural Strength.
When we talk about strength in odontoiatria, one of the most important numbers is resistenza alla flessione. What does that mean in simple terms? Imagine trying to bend a small beam of the material. The resistenza alla flessione is the amount of force, or pressure, it can take before it snaps. We measure this force in megapascals, or MPa. A higher MPa number means a stronger material. This is a critical property for any restauro that has to withstand chewing forces.
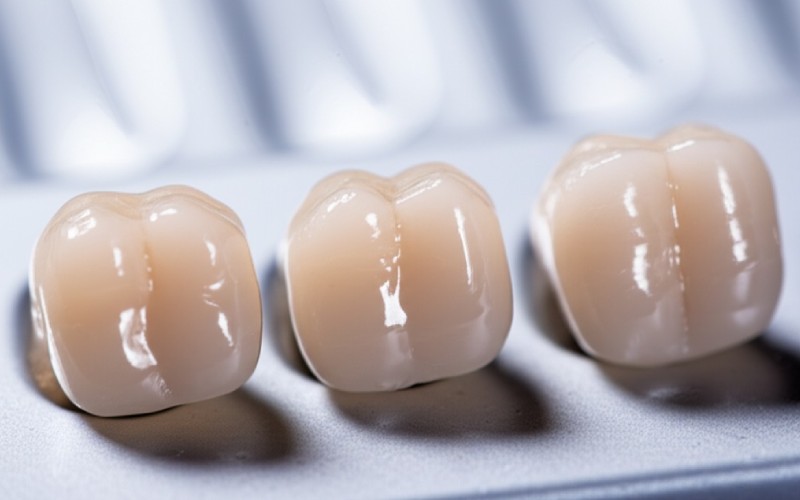
So, how does disilicato di litio stack up? The resistenza alla flessione di disilicato di litio ceramica is very impressive. Most Emax products have a resistenza alla flessione of around 400 to 500 MPa. To put that in perspective, older ceramica dentale might have a resistenza alla flessione of only 100-150 MPa. Ciò significa disilicato di litio is three to five times stronger. This high strength is why we can use it for a posteriore molare corona and trust it not to break under pressure.
Questo high flexural strength is a direct result of its internal structure. The dense, interlocking crystal network I mentioned earlier acts like rebar in concrete. It stops tiny cracks from growing and causing a fracture. This gives Emax e altri disilicato di litio ceramica the power to last for years, even in the tough environment of the mouth. The impressive resistenza alla flessione is a key reason why disilicato di litio has earned its place as a top-tier all-ceramic material. The modulus is also well-balanced.
What Are the Key Mechanical Properties of Lithium Disilicate?
Mentre resistenza alla flessione gets a lot of attention, it’s not the whole story. To truly understand a material, we need to look at all the mechanical properties of lithium disilicate. One of these is tenacità alla frattura. Think of tenacità alla frattura as a material’s resistance to an existing crack spreading. Disilicato di litio has excellent tenacità alla frattura due to its high crystal content. This makes the restauro more forgiving if a small flaw develops.
Another key property is the modulus of elasticity. The modulus is basically a measure of stiffness. A material with a very high modulus is very rigid, while one with a low modulus is more flexible. The modulus di disilicato di litio is similar to that of natural tooth dentin. This is a huge advantage. It means that when you bite down, the Emax corona flexes in a way that is very similar to a real tooth. This reduces stress on the underlying struttura del dente and the cement holding the corona in posizione.
Questi good mechanical properties combine to give disilicato di litio restauri their fantastic durata. Il properties of lithium disilicate glass-ceramics also include good thermal expansion characteristics and stabilità del colore. Ciò significa che il restauro won’t expand or contract too much with hot and cold foods, and it won’t change color over time. It’s this complete package of resistenza alla flessione, modulus, and toughness that makes disilicato di litio so reliable.
Can It Really Look Like a Real Tooth? (A Look at Translucency and Esthetics)
Strength is great, but in odontoiatria, looks matter just as much, especially for an anterior tooth. This is where disilicato di litio truly shines. The secret is a property called traslucenza. Traslucenza is the ability of a material to let some light pass through it, just like natural enamel.
Emax e altri disilicato di litio products come in various levels of traslucenza and opacity. For example, Ivoclar Vivadent makes ingots labeled HT (High Translucency) and LT (Low Translucency). An HT ingot is great for an inlay o un faccetta where you want the natural color of the tooth to show through. An LT ingot is better for a corona where you need to block out a dark underlying tooth. This control over optical properties allows a skilled technician to create a restauro with amazing, life-like esthetics.
Il estetico quality is not just about traslucenza. It’s also about how the material reflects light and the fine details that can be added. The surface of a disilicato di litio corona can be stained and glazed to perfectly mimic the subtle textures and colors of a real tooth. This level of artistry, combined with the material’s inherent estetico potential, is why disilicato di litio is the gold standard for beautiful restauri dentali. The final crystalline structure is key to these esthetics.
How Do You Make an Emax Restoration? (Press vs. Mill)
So how do we turn a piece of disilicato di litio into a perfectly fitting faccetta o corona? There are two main ways to fabbricare an Emax restauro: pressing and milling. Both methods are used all the time, and each has its own advantages. The choice often depends on the type of restauro and the equipment in the laboratorio odontotecnico.
The first method is the pressing technique, which uses products like IPS e.max Press. This is a bit like the classic “lost wax” technique. First, a wax model of the corona is made. This wax model is then surrounded by an investment material. After the wax is burned away, a small disilicato di litio ingot is heated until it becomes like thick honey. This molten glass-ceramic is then pressed into the mold. It’s a very precise way to fabbricare a restauro and is excellent for getting a perfect fit.
The second method is milling, which uses a CAD/CAM macchina. This is a high-tech approach. The tooth is scanned, either in the mouth (intraoral scanner) or from a model. A computer then designs the restauro, e un macchina carves the corona o faccetta out of a solid block of disilicato di litio materiale, such as an IPS e.max CAD block. This method is very fast and allows for same-day odontoiatria in some cases. You can mulino a beautiful all-ceramic corona in under an hour.
What’s the Real Difference Between IPS e.max Press and CAD?
At first glance, IPS e.max Press e IPS e.max CAD might seem like just two different ways to make the same thing. But there are some key differences in the materials themselves. The main difference is the state of the disilicato di litio when you start. The IPS e.max Press ingot is a fully crystallized lithium disilicate glass ceramic (Li2Si2O5). It already has its final, high resistenza alla flessione.
Il IPS e.max CAD block, on the other hand, is delivered in a partially crystallized state. It is a softer, bluish material made of lithium metasilicate crystals (Li2SiO3). This material has a much lower resistenza alla flessione, around 130 MPa, which makes it easy for the macchina a mulino quickly and without wearing out the tools. After the restauro is milled, it must go into a special oven for a firing cycle. This is the final crystallization step. During this firing, the lithium metasilicate (Li2SiO3) transforms into the much stronger disilicato di litio (Li2Si2O5), and the corona turns into the correct tooth color.
So, which one is better? It depends. IPS e.max Press is often said to have a slightly higher resistenza alla flessione (around 470 MPa vs. 400 MPa for CAD) and is preferred for more complex cases or a three-unit bridge. IPS e.max CAD offers incredible speed and convenience. Both methods, when done correctly, produce a fantastic and strong all-ceramic restauro. Il fabrication method is just a different path to the same excellent result.
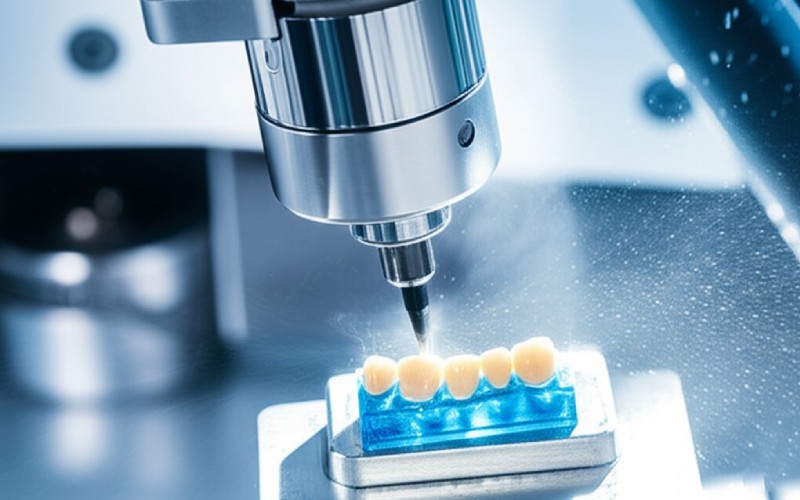

Are There Other Options Besides Emax? What About LiSi Press?
Mentre Ivoclar Vivadent and its Emax brand are the big names in disilicato di litio, they are not the only players in the game. Competition is a great thing in materiali dentali, and other companies have developed their own excellent lithium disilicate glass ceramics. One of the most well-known alternatives is GC’s LiSi Press. This is another pressable disilicato di litio that competes directly with IPS e.max Press.
LiSi Press boasts similar properties, including high resistenza alla flessione and beautiful esthetics. Some technicians love the way the LiSi Press ingot flows and the vitality they can get in their all-ceramic restorations. It uses a similar pressing technique and is designed to create a strong, monolitico restauro or be layered with porcellana for custom characterization. The existence of products like LiSi Press pushes all manufacturers to keep innovating and improving their ceramica dentale.
Whether a lab chooses Emax o LiSi Press often comes down to personal preference, experience, and relationships with the manufacturers. The important thing is that we have choices for high-strength materiali ceramici that allow us to provide the best possible care for our patients. This is a great time for periodontics and restorative work.
What’s the Secret on the Inside? (A Peek at the Microstructure)
I’ve mentioned the crystal structure a few times, but let’s take a closer look. The real secret to the resistenza alla flessione di disilicato di litio is its microstructure. Imagine a pile of needles thrown on a table. Now imagine filling all the space between those needles with glue. That’s a simple way to picture the microstructure in lithium disilicate glass. The “needles” are tiny, elongated crystals of disilicato di litio (Li2Si2O5). The “glue” is the glassy matrix that holds them all together.
This interlocking crystalline structure is incredibly effective at stopping cracks. When a force is applied to the corona, a tiny crack might start in the glass matrix. But as soon as it hits one of the many Li2Si2O5 crystal needles, it has to change direction. It gets deflected and blunted. To break the material, a crack would have to find a path through this dense, tangled forest of crystals. This gives the material its amazing tenacità alla frattura e resistenza alla flessione. The study of the crystallization and microstructure in lithium is fascinating.
The chemical process is also key. The heat treatment on crystallization is precisely controlled. Some research, like a vitro study on the effect of P2O5, shows how tiny additions of other chemicals can influence crystal growth. The p2o5 on the crystallization can affect the size and density of the crystals. All this science, from p2o5 and heat treatment to the final treatment on crystallization and microstructure, is done to create the ideal monolitico structure. It’s a world away from a weaker lithium silicate come li2sio3.
Is Lithium Disilicate the Right Choice for Everything?
It is not the perfect solution for every single situation. The biggest consideration is for long-span bridges, especially in the posteriore area of the mouth where biting forces are highest. While an Emax corona is great for a single posteriore tooth, a bridge that replaces two or more teeth requires even more resistenza alla flessione. Il connector areas of a bridge are where stress is concentrated.
For a long posteriore bridge, a stronger material like monolitico zirconia is often a better choice. Zirconia can have a resistenza alla flessione of over 1000 MPa, more than double that of disilicato di litio. However, zirconia typically has lower traslucenza, so it can be a trade-off between ultimate strength and the best esthetics. So, where is disilicato di litio the hero? It’s perfect for almost any single-tooth restauro. This includes anterior e posteriore crowns, veneers, inlays, and intarsi.
You can also fabbricare a short, three-unit bridge with disilicato di litio if it’s in the anterior region (front of the mouth). The decision always comes down to the specific clinical situation. We have to consider the patient’s bite (occlusal forces), the location in the mouth (anterior vs. posteriore), and the desired estetico outcome. But for the vast majority of all-ceramic single-unit restauri dentali, disilicato di litio materiale is a fantastic, reliable, and beautiful choice.
Cose da ricordare
- Strong and Beautiful:
Disilicato di litio(Emax,LiSi Press) offers a great mix ofresistenza alla flessione(400-500MPa) and life-likeesthetics. - Crystal Power: Its strength comes from a dense structure of interlocking
Li2Si2O5crystalneedles in a glassmatrix. - Versatile Use: It’s great for a single
corona,faccetta,inlay, eintarsiin both theanterioreposterioreparts of the mouth. - Two Ways to Make: Può essere
fabricated usingapressing technique(IPS e.max Press) or milled with a CAD/CAMmacchina(IPS e.max CAD). - Not for Everything: For long bridges in the back of the mouth, a stronger material like
zirconiais often a better choice.